Remotes in GitLab
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 0 minQuestions
How do I share my changes with others on the web?
Objectives
Explain what remote repositories are and why they are useful.
Push to or pull from a remote repository.
Version control really comes into its own when we begin to collaborate with other people. We already have most of the machinery we need to do this; the only thing missing is to copy changes from one repository to another.
Systems like Git allow us to move work between any two repositories. In practice, though, it’s easiest to use one copy as a central hub, and to keep it on the web rather than on someone’s laptop. Most programmers use hosting services like GitHub, Bitbucket or GitLab to hold those main copies; we’ll explore the pros and cons of this in a later episode.
1. Create a remote repository
Let’s start by sharing the changes we’ve made to our current project with the world. Log in to GitLab, then click on the “+” icon roughly in the middle, to create a new project (GitLab initializes at the “project” level rather than the “repository” level.) Select “New Project”:
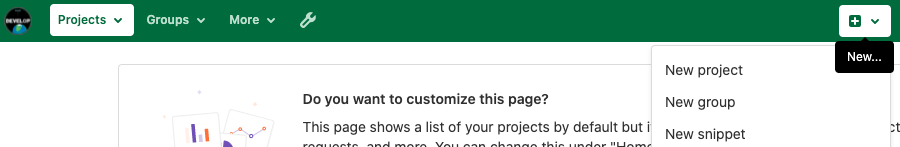
Then select “Create blank project”:
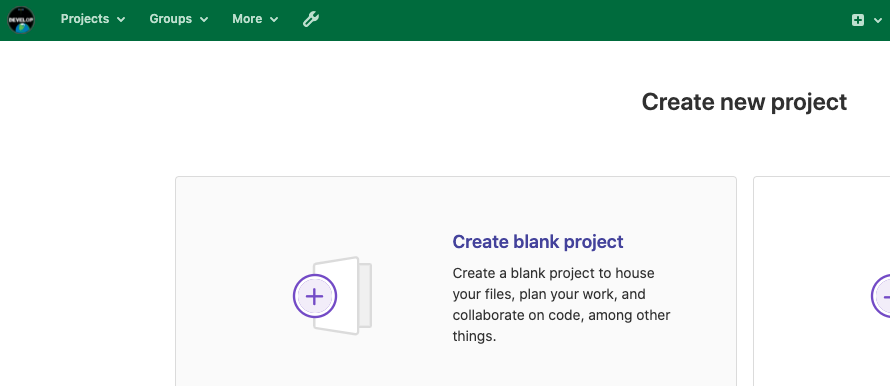
Name the project, and thus the repository, planets:
Note: Since this repository will be connected to a local repository, it needs to be empty. Leave “Initialize this repository with a README” unchecked, and keep “None” as options for both “Add .gitignore” and “Add a license.” See the “GitLab License and README files” exercise below for a full explanation of why the repository needs to be empty.
As soon as the repository is created, GitLab displays a page with a URL and some information on how to configure your local repository:
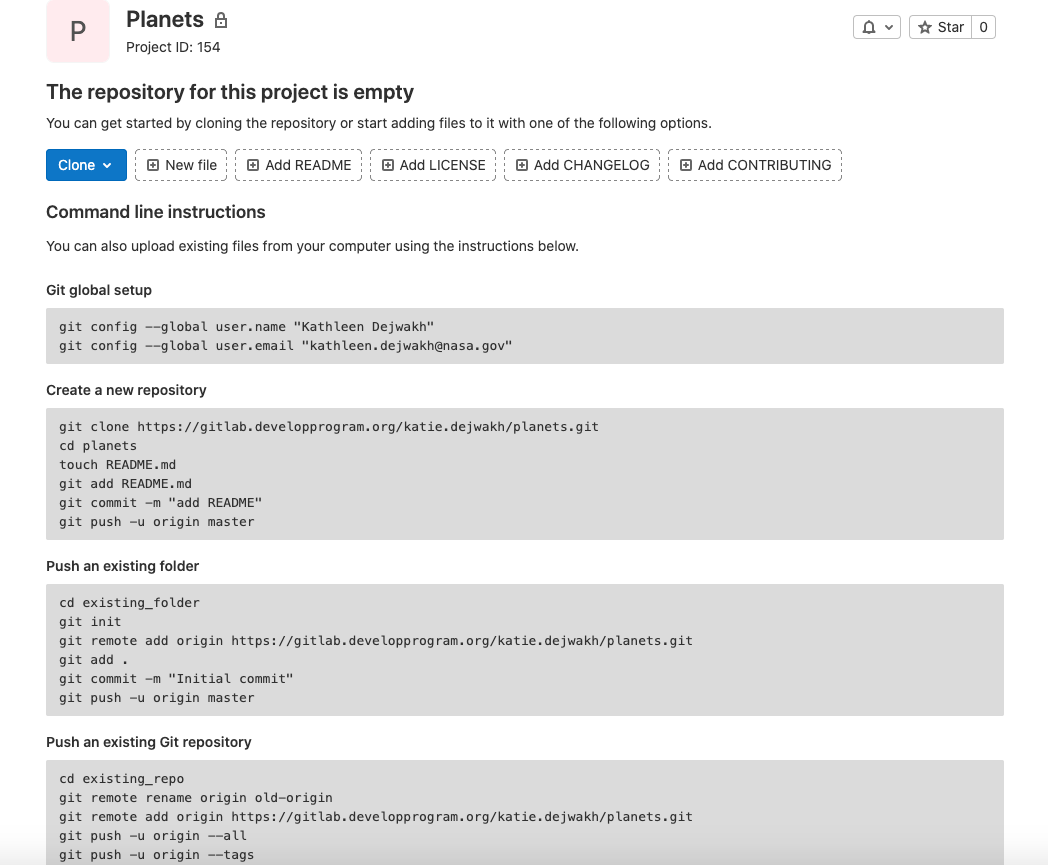
This effectively does the following on GitLab’s servers:
$ mkdir planets
$ cd planets
$ git init
If you remember back to the earlier episode where we added and
committed our earlier work on mars.txt, we had a diagram of the local repository
which looked like this:
Now that we have two repositories, we need a diagram like this:
Note that our local repository still contains our earlier work on mars.txt, but the
remote repository on GitLab appears empty as it doesn’t contain any files yet.
2. Connect local to remote repository
The next step is to connect the two repositories. We do this by making the GitLab repository a remote for the local repository. The home page of the repository on GitLab includes the string we need to identify it:

You also have the option of using the HTTPS protocol, but this may not work with DEVELOP’s GitLab instance at this time.
Copy the SSH URL from the browser, go into the local planets repository, and run
this command:
$ git remote add origin git@gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets.git
Make sure to use the URL for your repository rather than Vlad’s: the only
difference should be your username, “firstname.lastname,” instead of vlad.
origin is a local name used to refer to the remote repository. It could be called
anything, but origin is a convention that is often used by default in git
and GitLab, so it’s helpful to stick with this unless there’s a reason not to.
We can check that the command has worked by running git remote -v:
$ git remote -v
origin git@gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets.git (push)
origin git@gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets.git (fetch)
We’ll discuss remotes in more detail in the next episode, while talking about how they might be used for collaboration.
Once the remote is set up, this command will push the changes from our local repository to the repository on GitLab:
$ git push origin main
Since Dracula set up a passphrase, it will prompt him for it. If you completed advanced settings for your authentication, it will not prompt for a passphrase.
Enumerating objects: 16, done.
Counting objects: 100% (16/16), done.
Delta compression using up to 8 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (11/11), done.
Writing objects: 100% (16/16), 1.45 KiB | 372.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 16 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (2/2), done.
To gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets.git
* [new branch] main -> main
Proxy (for HTTPS Usage)
If the network you are connected to uses a proxy, there is a chance that your last command failed with “Could not resolve hostname” as the error message. To solve this issue, you need to tell Git about the proxy:
$ git config --global http.proxy http://user:password@proxy.url $ git config --global https.proxy https://user:password@proxy.urlWhen you connect to another network that doesn’t use a proxy, you will need to tell Git to disable the proxy using:
$ git config --global --unset http.proxy $ git config --global --unset https.proxy
Password Managers
If your operating system has a password manager configured,
git pushwill try to use it when it needs your username and password. For example, this is the default behavior for Git Bash on Windows. If you want to type your username and password at the terminal instead of using a password manager, type:$ unset SSH_ASKPASSin the terminal, before you run
git push. Despite the name, Git usesSSH_ASKPASSfor all credential entry, so you may want to unsetSSH_ASKPASSwhether you are using Git via SSH or https.You may also want to add
unset SSH_ASKPASSat the end of your~/.bashrcto make Git default to using the terminal for usernames and passwords.
Our local and remote repositories are now in this state:
The ‘-u’ Flag
You may see a
-uoption used withgit pushin some documentation. This option is synonymous with the--set-upstream-tooption for thegit branchcommand, and is used to associate the current branch with a remote branch so that thegit pullcommand can be used without any arguments. To do this, simply usegit push -u origin mainonce the remote has been set up.
We can pull changes from the remote repository to the local one as well:
$ git pull origin main
From gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets
* branch main -> FETCH_HEAD
Already up-to-date.
Pulling has no effect in this case because the two repositories are already synchronized. If someone else had pushed some changes to the repository on GitLab, though, this command would download them to our local repository.
GitLab GUI
Browse to your
planetsrepository on GitLab. Under the Repository heading in the menu on the left, click the “Commits” heading. Investigate this page. What information can you gather/explore from these buttons? How would you get that same information in the shell?Solution
The middle button (with the picture of a clipboard) copies the full identifier of the commit to the clipboard. In the shell,
git logwill show you the full commit identifier for each commit.When you click on the hyperlinked commit message, you’ll see all of the changes that were made in that particular commit. Green shaded lines indicate additions and red ones removals. In the shell we can do the same thing with
git diff. In particular,git diff ID1..ID2where ID1 and ID2 are commit identifiers (e.g.git diff a3bf1e5..041e637) will show the differences between those two commits.The right-most button lets you view all of the files in the repository at the time of that commit. To do this in the shell, we’d need to checkout the repository at that particular time. We can do this with
git checkout IDwhere ID is the identifier of the commit we want to look at. If we do this, we need to remember to put the repository back to the right state afterwards!
Uploading files directly in GitLab browser
GitLab also allows you to skip the command line and upload files directly to your repository without having to leave the browser. There are two options. First you can click the “Upload files” button in the toolbar at the top of the file tree. Or, you can drag and drop files from your desktop onto the file tree. You can read more about this on this GitLab page
GitLab Timestamp
Create a remote repository on GitLab. Push the contents of your local repository to the remote. Make changes to your local repository and push these changes. Go to the repo you just created on GitLab and check the timestamps of the files. How does GitLab record times, and why?
Solution
GitLab displays timestamps in a human readable relative format (i.e. “22 hours ago” or “three weeks ago”). However, if you hover over the timestamp, you can see the exact time at which the last change to the file occurred.
Push vs. Commit
In this episode, we introduced the “git push” command. How is “git push” different from “git commit”?
Solution
When we push changes, we’re interacting with a remote repository to update it with the changes we’ve made locally (often this corresponds to sharing the changes we’ve made with others). Commit only updates your local repository.
GitLab License and README files
In this section we learned about creating a remote repository on GitLab, but when you initialized your GitLab repo, you didn’t add a README.md or a license file. If you had, what do you think would have happened when you tried to link your local and remote repositories?
Solution
In this case, we’d see a merge conflict due to unrelated histories. When GitLab creates a README.md file, it performs a commit in the remote repository. When you try to pull the remote repository to your local repository, Git detects that they have histories that do not share a common origin and refuses to merge.
$ git pull origin mainwarning: no common commits remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done. From git@gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets * branch main -> FETCH_HEAD * [new branch] main -> origin/main fatal: refusing to merge unrelated historiesYou can force git to merge the two repositories with the option
--allow-unrelated-histories. Be careful when you use this option and carefully examine the contents of local and remote repositories before merging.$ git pull --allow-unrelated-histories origin mainFrom git@gitlab.developprogram.org:vlad/planets * branch main -> FETCH_HEAD Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy. README.md | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 README.md
Key Points
A local Git repository can be connected to one or more remote repositories.
Use the SSH protocol to connect to remote repositories.
git pushcopies changes from a local repository to a remote repository.
git pullcopies changes from a remote repository to a local repository.